One saturday morning I was having a breakfast and I discovered face_recognition project. I started to play with the opencv example. I put my picture and, Wow! It works like a charm. It’s pretty straightforward to detect my face and also I can obtain the face landmarks. One of the landmark that I can get is the nose tip. Playing with this script I realized that with the nose tip I can determine the position of the face. I can see if my face is align to the center or if I move it to one side. As well as I have a new iot device (one ESP32) I wanted to do something with it. For example control a servo (SG90) and moving it from left to right depending on my face position.
First we have the main python script. With this script I detect my face, the nose tip and the position of my face. With this position I will emit an event to a mqtt broker (a mosquitto server running on my laptop).
import face_recognition
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
gonzalo_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("gonzalo.png")
gonzalo_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(gonzalo_image)[0]
known_face_encodings = [
gonzalo_face_encoding
]
known_face_names = [
"Gonzalo"
]
RED = (0, 0, 255)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
BLUE = (255, 0, 0)
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
face_names = []
process_this_frame = True
status = ''
labelColor = GREEN
client = mqtt.Client()
client.connect("localhost", 1883, 60)
while True:
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
# Resize frame of video to 1/4 size for faster face recognition processing
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
# Convert the image from BGR color (which OpenCV uses) to RGB color (which face_recognition uses)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1]
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_landmarks_list = face_recognition.face_landmarks(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding, face_landmarks in zip(face_encodings, face_landmarks_list):
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
name = "Unknown"
if True in matches:
first_match_index = matches.index(True)
name = known_face_names[first_match_index]
nose_tip = face_landmarks['nose_tip']
maxLandmark = max(nose_tip)
minLandmark = min(nose_tip)
diff = math.fabs(maxLandmark[1] - minLandmark[1])
if diff < 2:
status = "center"
labelColor = BLUE
client.publish("/face/{}/center".format(name), "1")
elif maxLandmark[1] > minLandmark[1]:
status = ">>>>"
labelColor = RED
client.publish("/face/{}/left".format(name), "1")
else:
status = "<<<<"
client.publish("/face/{}/right".format(name), "1")
labelColor = RED
shape = np.array(face_landmarks['nose_bridge'], np.int32)
cv2.polylines(frame, [shape.reshape((-1, 1, 2)) * 4], True, (0, 255, 255))
cv2.fillPoly(frame, [shape.reshape((-1, 1, 2)) * 4], GREEN)
face_names.append("{} {}".format(name, status))
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
# Scale back up face locations since the frame we detected in was scaled to 1/4 size
top *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
left *= 4
if 'Unknown' not in name.split(' '):
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), labelColor, 2)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, bottom - 35), (right, bottom), labelColor, cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
else:
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), BLUE, 2)
cv2.imshow('Video', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
video_capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Now another Python script will be listening to mqtt events and it will trigger one event with the position of the servo. I know that this second Python script maybe is unnecessary. We can move its logic to esp32 and main opencv script, but I was playing with mqtt and I wanted to decouple it a little bit.
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
class Iot:
_state = None
_client = None
_dict = {
'left': 0,
'center': 1,
'right': 2
}
def __init__(self, client):
self._client = client
def emit(self, name, event):
if event != self._state:
self._state = event
self._client.publish("/servo", self._dict[event])
print("emit /servo envent with value {} - {}".format(self._dict[event], name))
def on_message(topic, iot):
data = topic.split("/")
name = data[2]
action = data[3]
iot.emit(name, action)
client = mqtt.Client()
iot = Iot(client)
client.on_connect = lambda self, mosq, obj, rc: self.subscribe("/face/#")
client.on_message = lambda client, userdata, msg: on_message(msg.topic, iot)
client.connect("localhost", 1883, 60)
client.loop_forever()
And finally the ESP32. Here will connect to my wifi and to my mqtt broker.
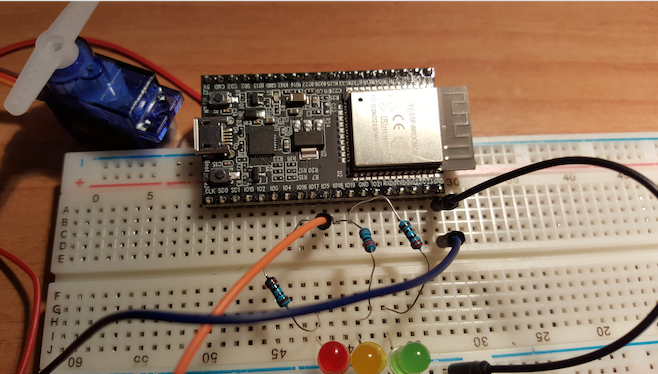
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
#define LED0 17
#define LED1 18
#define LED2 19
#define SERVO_PIN 5
// wifi configuration
const char* ssid = "my_ssid";
const char* password = "my_wifi_password";
// mqtt configuration
const char* server = "192.168.1.111"; // mqtt broker ip
const char* topic = "/servo";
const char* clientName = "com.gonzalo123.esp32";
int channel = 1;
int hz = 50;
int depth = 16;
WiFiClient wifiClient;
PubSubClient client(wifiClient);
void wifiConnect() {
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print("*");
}
Serial.print("WiFi connected: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void mqttReConnect() {
while (!client.connected()) {
Serial.print("Attempting MQTT connection...");
if (client.connect(clientName)) {
Serial.println("connected");
client.subscribe(topic);
} else {
Serial.print("failed, rc=");
Serial.print(client.state());
Serial.println(" try again in 5 seconds");
delay(5000);
}
}
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
Serial.print("Message arrived [");
Serial.print(topic);
String data;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data += (char)payload[i];
}
int value = data.toInt();
cleanLeds();
switch (value) {
case 0:
ledcWrite(1, 3400);
digitalWrite(LED0, HIGH);
break;
case 1:
ledcWrite(1, 4900);
digitalWrite(LED1, HIGH);
break;
case 2:
ledcWrite(1, 6400);
digitalWrite(LED2, HIGH);
break;
}
Serial.print("] value:");
Serial.println((int) value);
}
void cleanLeds() {
digitalWrite(LED0, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED1, LOW);
digitalWrite(LED2, LOW);
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
ledcSetup(channel, hz, depth);
ledcAttachPin(SERVO_PIN, channel);
pinMode(LED0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED2, OUTPUT);
cleanLeds();
wifiConnect();
client.setServer(server, 1883);
client.setCallback(callback);
delay(1500);
}
void loop()
{
if (!client.connected()) {
mqttReConnect();
}
client.loop();
delay(100);
}
Here a video with the working prototype in action
The source code is available in my github account.


